11 Ways to Improve your SEO Rankings on Google
Over 8.5 billion searches are made on Google each day. It’s therefore no surprise that Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) has quickly become a mandatory tactic in today’s digital marketing landscape. When done right, SEO is cost-efficient and wholly effective.
Whether you’re starting out in your business, marketing campaign, or have been around for a while, SEO is an evergreen marketing technique that ensures the longevity and relevancy of your brand.
Did you know that most people never make it to the 2nd page of a search result? This could be worrying, because if you’re not the first result, or even on the 1st page of the search results, you are potentially missing out on a lot of traffic and possible customers.
In this article, we will go through the 11 ways you can improve your SEO and therefore, site ranking.
- Conducting Keyword Research to Optimise Your Webpage Content
- Improve the Title Tags, Meta Descriptions and URLs
- Apply Proper Header Tags
- Improve Your Site Speed
- Follow the Rule of E.A.T.
- Keep Your Website Content Up to Date
- Build Backlinks
- Build Internal Links
- Optimise Images and Videos
- Set Up Google My Business
- Optimise for Voice Search

1. Conducting Keyword Research to Optimise your Webpage Content
Keywords are how people search for you on search engines, primarily Google (92.49% of market share). This is where we put ourselves in our customers’ shoes. How would they search for your product? What words, or search queries would they use?
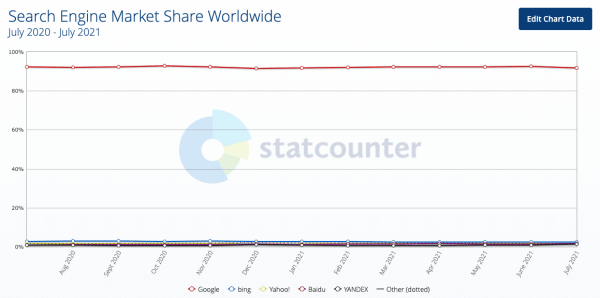
StatCounter GlobalStats June 2021. Source: https://gs.statcounter.com/search-engine-market-share
Keywords or keyword phrases should be conversational and relevant to your business. For example, if you’re selling office chairs in Singapore, common search queries might include:
- Best office chairs
- Best office chairs Singapore
- Office chairs Singapore
- Buy office chairs Singapore
Remember, the key is to put yourself in your customers’ shoes when deciding what keywords to use. Of course, you’ll then have to decide if it’s worth ranking for those keywords. This is where keyword research tools come in – a free tool you can use is Google Keyword Planner (Note: you’ll need to have a Google Adwords account created first).
Keywords Planner
Businesses use Keyword Planner to find relevant and specific keywords to use for SEO campaigns.
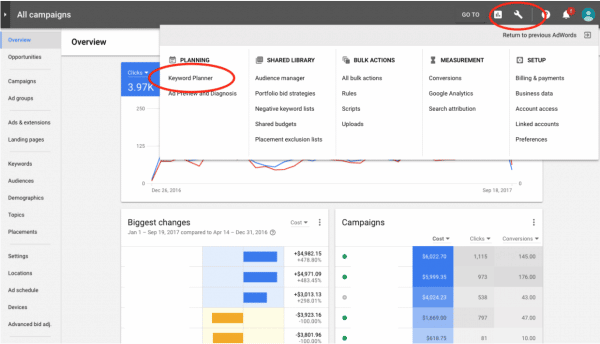
GoogleAds Keyword Planner. Source: https://www.webascender.com/blog/how-to-use-google-adwords-keyword-planner-to-find-keywords-that-convert-step-by-step/
Once you have chosen your keywords, there are 3 questions that you should consider:
a. Can the keyword phrase(s) be used in my page URL?
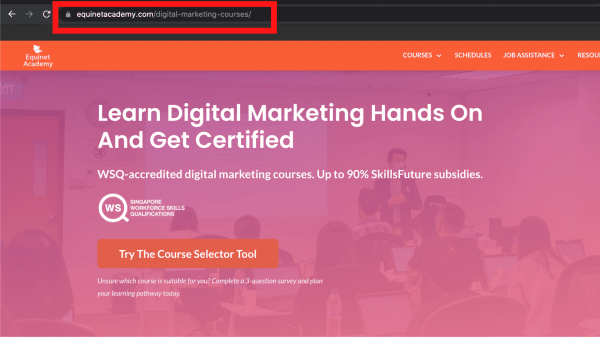
For example, take a look at Equinet’s courses page in the screenshot above. One of our top keywords is “digital marketing courses” and we have included that into our URL for this page.
b. Can the keyword phrase(s) be used in the page title?
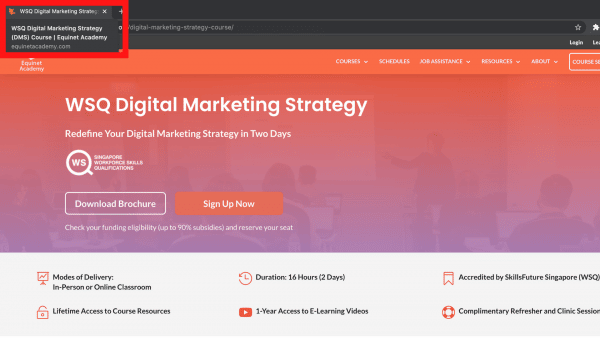
Another one of Equinet’s keywords is “digital marketing strategy” and we have incorporated this keyword in the page title of our Digital Marketing Strategy course, as can be seen in the screenshot above.
c. Can the keyword phrase(s) be used in page headings and subheadings?
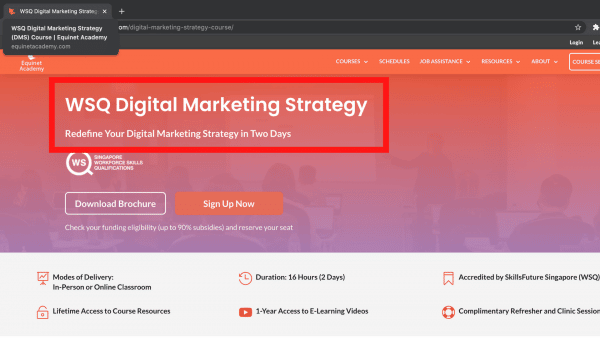
On the same page, we also include the keywords “digital marketing strategy” in our page headings and subheadings, as can be seen in the screenshot above.
This will serve as a guide to help you ensure the quality of your keywords, and their positioning throughout your site.
For example, using the example of an e-commerce website selling office chairs, you could use phrases in your product pages such as:
1) Buy office chair
2) Best office chairs near me
3) Office chairs Singapore
4) Cheap and best office chairs
It is crucial to conduct keyword research in order to effectively implement SEO and gain a higher site ranking. If you’d like pro keyword research and analysis tips, here are 4 for you.
2. Improve Title Tags, Meta Descriptions and URLs
Among the list of key factors that will increase your SEO rankings is the optimisation of your title tags and meta descriptions with the keywords found from keyword research.
Title tags are the first 65 characters you see for listings on SERPs.

What a title tag looks like
The most important part of the headline usually contains the keywords relevant to the site, but the rest cuts off. So, it’s really best to keep it short while also enabling the user to know what your site is about.
According to the Nielsen Norman Group (NN/g), a UX research and consulting firm, users only ever scan the first 2 words of a search result, so your message has to be eye-catching, relevant, and to the point. But don’t compromise clarity. Your title and your site content must correlate.
Now, meta descriptions, otherwise known as snippets, are what you see below the title tags. They basically add on to your title by describing it.

Meta description is the text below the title tag.
Being descriptive but concise goes a long way in helping users understand that you have what they are looking for. It pays to shape them to answer “Who? What? Why? Where? When? How?” questions. That way, you ease the transition to your site.
But remember, just like your title tags, there’s a word limit too. Google allows for up to 160 characters.
Does all this sound like too much? Don’t worry, Google has shared some advice on how to improve them here.
If your title tags and meta descriptions are clear and able to grab your audience’s attention, you’ll see an increase in clickthrough rates and site traffic; both of which could contribute to a better SERP ranking.
URLs, like title tags and meta descriptions, are straight to the point. It is usually optimised with the keywords that enable you to be found on SERPs, which is why URLs are very important in increasing your site ranking.
By properly structuring your URLs, you give users an incentive to click on your link, because they know you are relevant to them and that you have the answers they are looking for.
Standardise your different URLs to keep them clean and easily decipherable.
Here’s how you can do that:
- Page URLs are the identity of your site. Take your time to customise them according to your keywords and site content.
- Keeping it short and simple allows for easier accessibility to your site. Remove any use of stop words such as “a”, “the”, “or”, “but”, “an”, etc. Keep that space for the important stuff
- Now remember your primary keyword; this is especially important because it will affect your SEO rankings. Make use of it in your URL.
- It is especially good practice to use hyphens to separate the words in your URL, because this alerts the search bots where the breaks are in your sentences, and also allows your users to better understand your URL. How does https://www.equinetacademy.com/what-is-content-marketing-definition-benefits-and-examples/ look as compared to https://www.equinetacademy.com/whatiscontentmarketingdefinitionbenefitsandexamples/?
- Some sites can have multiple URLs for the same page. www.equinetacademy.com and equinetacademy.com both land on the same page. To remove the possibility of diluting your SEO value, it is best to consolidate everything under a single address.
3. Apply Proper Header Tags
What exactly are header tags, and how do they contribute to SEO?
Also known as heading tags, they are commonly used on webpages to show distinction between headings and subheadings. These are ranked with numbers, from 1 to 6 in order of importance. Both page readability and SEO rely on header tags.
How so?
They give a necessary structure to your content, and give users direction toward the ideas, and themes found in your content while simultaneously including the keywords you are trying to rank for, so that search engine algorithms can understand your content better in order to rank them.
When you enable users to quickly find what they are looking for, it leads to reduced bounce rates, which search engines take note of. As such, your rankings will increase.
So, when designing your tags, follow this rule: Think of your user and what you can do to make their experience easier.
Here’s a brief overview of definitions for header tags (the H stands for heading element, though we stick to header tags):
- H1 – Title of your post. These are meant to be attention-grabbing, descriptive of what the content or site is all about, and centred around keywords.
- H2 – The subheadings that denote which are the main points for your content, and help to separate the sections. A tip you can use is to correlate them to your H1 while also still being identifiable to the users.
- H3 – These are the subsections below your H2. Consider using them in point form or in a list.
- H4 – Basically the same function for H3, that it serves to H2. Also consider using them in point form or in a list.

The basic hierarchy between header tags. Source: https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/header-tags
A recommendation would be to ensure all your header tags contain keywords and that are strategically placed around your site.
To use the same example as before, let’s say you’re selling office chairs. Now you’d definitely want the audience to know what your business is about, so for your H1 you would have something like ‘Top 10 Quality Office Chairs and Where to Find Them’.
As for your H2, longtail keywords can be added in. So, you could have something along the lines of ‘5 Ways to Check Quality of Office Chairs’, or ‘The Top 3 Things to Look Out For When Selecting An Office Chair’. These further cement the relevancy of your site and business to the right audience.
So, in summary, header tags have a lot of weight when it comes to helping audiences find and understand your site/business, because they affect your site traffic, bounce rates, and ultimately, your SERP rankings.
4. Improve your Site Speed
According to Quicksprout, a business advisory firm, 40% of users do not wait for more than 3 seconds for a web page to load, with a total of 80% not ever returning to that site again. Users have a harder time engaging with slow websites, which leads to a higher abandonment rate, thereby affecting your SEO.
Additionally, Google has used site speed as a ranking factor since 2010 and its importance was increased after the introduction of the “Speed Update” in 2018, which affects mobile search ranking. As such, your site speed directly contributes to your site ranking on Google and should always be taken into consideration.
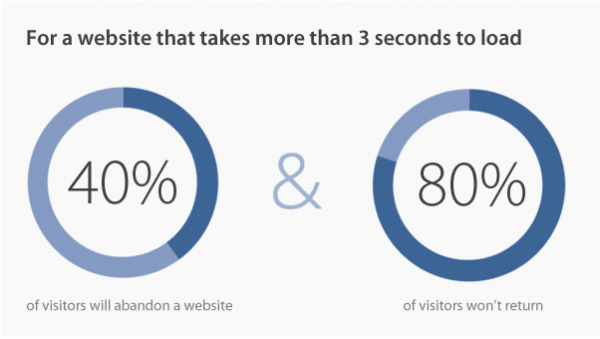
Abandonment of Pages due to loading time. Source: https://www.vpnmentor.com/blog/vital-internet-trends/#Website-Performance
Google also takes into consideration desktop and mobile capability when ranking pages. You could have your site optimised for desktop but not for mobile, and your overall page ranking will still drop in the mobile search results. Here are a couple of common tools you can use to do a site speed check:
a. Pingdom
Pingdom checks the speed of your website and diagnoses what needs work. Additionally, it helps to test your site’s accessibility and speed from different locations in the world.
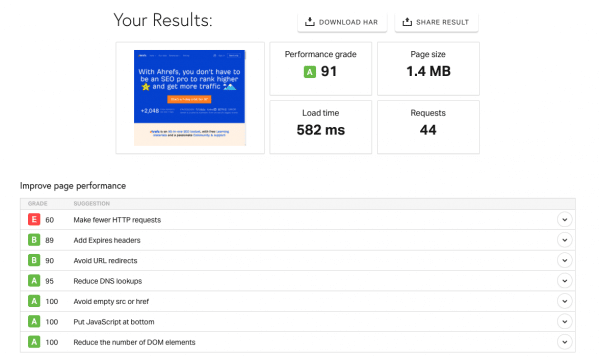
Site Speed Check for AhRefs. Source: https://tools.pingdom.com/#5e9f9b66a7000000
Above is the site speed check for AhRefs using Pingdom. Do take note of the parameters used. While it may look confusing, they have a step-by-step guide on what to look out for.
b. PageSpeed Insights
We have Google’s free-to-use PageSpeed Insights tool, which enables you to do a speed check on your site.
The drawback however, is that the checks have to be done for each individual page. If you use this tool, our recommendation would be to prioritise the pages which get the most traffic, as those will readily benefit from any optimisation efforts. You can find out which pages get high traffic via Google Analytics.
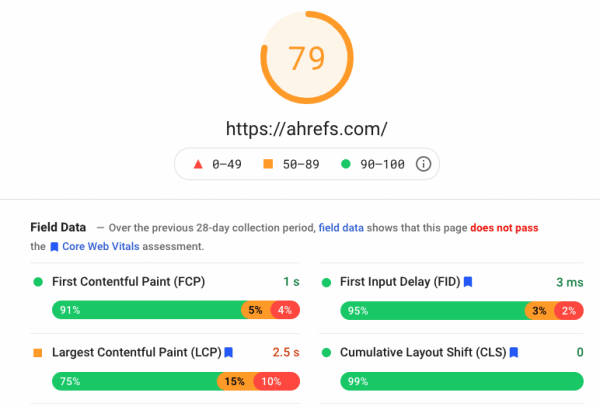
Speed Score for AhRefs.com Source: https://developers.google.com/speed/pagespeed/insights/?url=ahrefs.com&tab=desktop
As you can see, a website’s performance score is based on 4 factors.
These are:
First Contentful Paint (FCP):
This measures content loading performance. For a good user experience, pages should generally have FCPs of 3 seconds or less.
First Input Delay (FID):
This measures site interactivity. Pages which provide a good user experience usually have FIDs of less than 100 milliseconds.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP):
This assesses page loading performance. When the page first starts loading, LCP should generally occur within 2.5 seconds.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS):
This measures the visual stability of a site. For a good user experience, a CLS of 0.1 or less should be maintained.
c. The types and number of plug-ins
Lastly, one other thing that can affect site speed but is often overlooked is the type and number of plug-ins on your pages. Plug-ins are good to have on any page, but they do take up a fair bit of space as well. So, it would be prudent to keep track of them and substitute or remove them if necessary. It pays to do regular checks to ensure that they are working optimally.
5. Follow the Rule of E.A.T
The acronym E.A.T. stands for: Expertise, Authority, and Trust. Created by Google, it is derived from their Search Quality Rating Guidelines and refers to how they rank websites in their SERP. Essentially, these are the basic guidelines that Google uses and that all websites should follow, in order to create a high-quality website that ranks well. E.A.T isn’t measured in the way that site speed can be measured. Rather, it judges content from a user’s standpoint.
Expertise
Expertise refers to having a high level of knowledge, skill or achievement in a specific field. This typically refers to the content being held on a website, and not the actual organisation or website itself. Google ranks this by looking for content created by a subject matter expert.
For certain topics, such as financial or medical advice, content should be created by people who are credible professionals in that sector or industry. For more general topics that require less formal expertise, Google also considers everyday experiences under expertise.
Otherwise, Google will determine your website as hosting content that does not hold a sufficient level of expertise, which could lead to your website ranking lower on the SERP.
To put it simply, depending on the type of content you host on your website, ensure that there is a certain level of expertise being associated with it.
Authority
Authority in E.A.T is all about reputation. If a website is seen as the go-to for information or resources about a specific topic, that website holds authority.
So, how does Google discern authority of your website? Basically, it conducts reputation research. It searches across the web for mentions of your company or website that were not created by you, your company, or your website. It looks for independent sources, like news articles, reviews or recommendations and rates you accordingly.
Trust
Trust refers to the legitimacy and accuracy of a website and the content it hosts. If a website is trustworthy, in Google’s eyes, it ranks better on the SERP.
Google checks for this through a variety of ways like whether a website credits who is responsible for a piece of content (which also ties back with expertise) or whether they provide credible and trustworthy sources within their content.
Trustworthiness in a website is incredibly important to both Google and your users.
E.A.T is an important factor in SEO that you should always keep in mind and always continuously try to improve. When your website maintains all three factors, Google recognises this and ranks your website accordingly.
6. Keep your Website Content Up to Date
Content. Is. King.
This has always been one of the most important commandments in marketing – and with good reason.
Your content is one of the biggest factors that makes your brand/site attractive and relevant. It’s what brings in site traffic, and ultimately, affects your SEO rankings.
If you’re familiar with how search engines work, you would know that Google’s search engine algorithms are constantly crawling through existing web pages and looking for new content to index.
They can recognise when a page is fresh and a website is actively updated, which leads to more content being indexed and, potentially, a higher site ranking. Additionally, the more often you publish new content, your site will be re-indexed which also improves site ranking.
Update your content
One of the ways to look out for diminishing quality of older content is to monitor traffic to each of your pages, and take note of any drops or bounces – which could mean information on that page is stale.
This can be done via the keywords your site is tagged for, and to monitor the statistics.
For example, Ahrefs realised that the traffic had been consistently dropping on one of their previously well-performing articles, a list of the top 100 Google searches. They performed a content audit, a process where you analyse all the content hosted on a website, and found that the content had to be updated.
As seen in the graphic below, the traffic for this particular article had dropped to less than 5000 visitors per month but, once they updated the article, it increased to an average of 14,555 visitors per month. This is just one example of many that shows the importance of keeping your content fresh and updated.
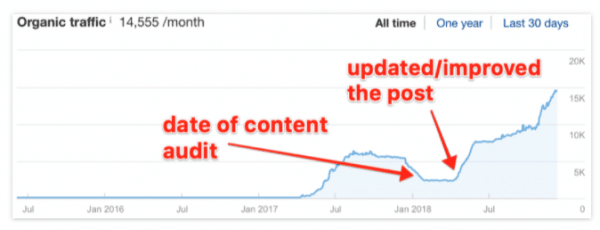
The effect updating your content can have on your site’s ranking. Source: https://ahrefs.com/blog/how-to-improve-seo/
One handy tool to analyse your site’s content is Content Explorer. It’s a great tool which helps you to look through any stale content on your website, broken backlinks, relevant keywords your competitors use, as well as to sift through web pages that are similar and relevant to yours.
You can additionally choose to reverse engineer your competitors’ content marketing strategies, and use them to your advantage.
But remember, your content has to be fresh, have quality and be relevant. Having such content will increase your site’s dwell time.
Dwell Time
According to Search Engine Journal, a search marketing content online publication, dwell time is how long a user spends on your webpage after clicking on it in the SERPs.
So, how does this translate to your SEO ranking?
With fresh and relevant content, your site will hold users for longer, and Google’s algorithms take note of this. Remember E.A.T?
But be careful – too many changes to your site’s content can possibly restart your rankings. The trick is to make the changes steadily, not all at once. It’s usually best to develop a schedule to review and update your content, so that you don’t risk having your rankings drop, or worse, restart.
7. Build Backlinks
Getting other websites to link to yours is known as the process of building backlinks.
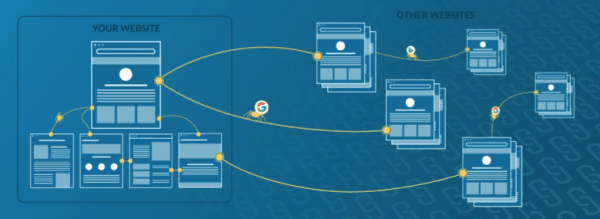
How Google uses links. Source: https://moz.com/beginners-guide-to-link-building
The more links that search engines discover lead back to your page (backlinks) from reputable sites, the higher the ranking of your page will be. Quality backlinks show users and search engines that reputable sites trust your site and find its content relevant to the topic(s) at hand, which would result in your SEO rankings improving.
A metric that measures the number of backlinks is Domain Authority. Although this is not a metric used by Google to measure site ranking, it is an important metric used to assess how well your website is performing as compared to your competitors.
A Domain Authority score is a number between 1 – 100, with a higher number meaning a better Domain Authority. It takes into account the quantity and quality of backlinks of a webpage and values it accordingly.
If you want to check the Domain Authority of your website, you can do so here for free.
How to build backlinks
For starters, your site has to have relevant, fresh and high-quality content that meets Google’s E.A.T standards– remember, you want reputable sites to give you their stamp of approval by linking to your site.
Next, begin reaching out to reputable sites with a strong pitch– sharing your site traffic/rankings might help.
Other ways to get backlinks include guest blogging, and collaborating with influencers and industry leaders, all while consistently producing quality content.
Lastly, make it a point to fix any broken links on your site. These can unwittingly hurt site traffic, because as good as your content may be, broken links lead to users dropping off from your site.
For a more in-depth look into building quality backlinks, give this article a read.
8. Build Internal Links
Internal links refer to links on your website that direct you to another page on your website. Both visitors to your website and search engines use these internal links to find content and navigate through your website. If a page isn’t linked anywhere else, it will never be found by visitors or search engines.
There are many types of internal links, such as the ones in your homepage (Menu, About Us, Shop etc.) and contextual links, which are links within the content hosted on your website.
Contextual links in particular are important as they point users towards relevant content and allow search engines to determine what content on your site is related. When a specific page contains more links, search engines will deem it more valuable and important, which in turn boosts your SEO rankings.
For example, if you feature a blog on your website, you should look to add contextual links within each article to direct users to another article with any relevant information. Additionally, think about adding a “Related Posts” feature on your articles, which would consolidate relevant content for your users to click through.
How to check Internal Links
We would recommend using Yoast SEO, which is a free tool that has several features to help you improve on your internal linking. One feature analyses your website’s content to determine whether you have internal links built and another also counts the number of internal links you might have on a specific page. This way, you know which areas of your website would require more internal link building.
9. Optimise Images and Videos
It’s no secret that the best way to capture attention is usually with stunning visuals and imagery. But sadly, this is often overlooked. Here are some examples of sites with poor visuals so you know what to avoid.
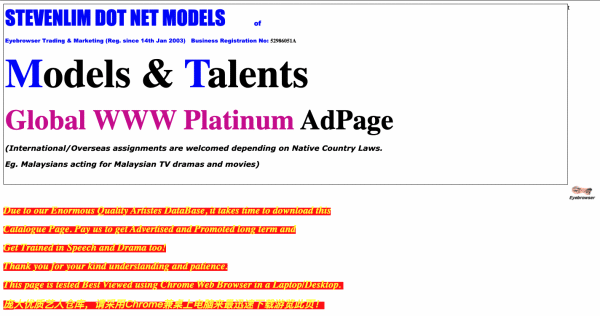
A landing page with poor visuals. Source: http://stevenlim.net/models2.htm

Confusing layout and poor choice of imagery and colour scheme. Source: https://www.leadpages.com/blog/see-worst-landing-page-ever-created-10-reasons/
Poor imagery can cause a slew of problems for websites and businesses. They can slow down page loading speeds, reduce site dwell times, limit SEO rankings and generally slow down site traffic.
Optimised images, on the other hand, can help a great deal in attracting traffic to your site. They can also save you space because, as the famous saying goes, a picture paints a thousand words.
What this basically means is that appropriate and optimised images could help to:
- Simplify a huge chunk of text
- Add context to content
- Give way to better understanding of written content
- Get on track with Google’s intent for visual searching
For large images, the key is to resize or compress them. Consider adding in your SEO keywords into title tags for your images. When you do so, you also gain traffic from Google Image search results.
For example, if you were selling office chairs, instead of naming your image “chair1”, try naming it “best office chairs” instead. If someone searches for the “best office chairs” on Google Images, your image would appear in the search results. This would become another channel for generating traffic to your site.
As for alt text for your images, try to follow these key points:
- Be Descriptive. Describe your image as best as you can. Add context to the content, and this will help rank your images in Google Image Search.
- Make it Distinctive. While adding your keywords to your images, try to use them in a manner that is descriptive of the images.
- Stay Relevant. The alt text should directly correlate to the image, and not spiral off-topic
10. Set up Google My Business
Did you know that an average business gets 943 Search views and 317 Map views a month?
Google My Business (GMB) is a very important asset that most businesses today are only just discovering. Think YellowPages but much larger and more accessible.
It’s basically a directory for businesses, listing all the information about them that customers need to know. Business hours, industry, services, and location are just some of the information that is made readily available to the public.
Here is how to get it started with Google My Business.
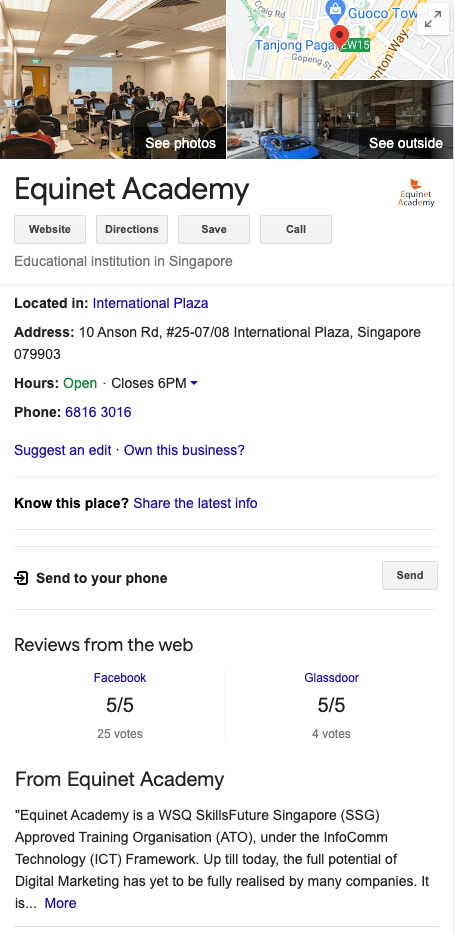
Equinet Academy’s Listing with GMB
By registering your business with GMB, you will be automatically added to Google Maps as a business– adding another channel through which you gain exposure to your business.
Local search results are based on 3 key factors for Google Maps: Relevance, Distance, Prominence.
- Relevance: the match between a user’s intent and a listing
- Distance: proximity between users and verified businesses
- Prominence: basically, how well known your business is.
When these 3 factors are consistently met, a site would be ranked in the top 3 search results on Google Maps, called the “local 3 pack”– thereby boosting your SEO rankings.
It might be quite the challenge to manage so many channels, but the ease at which your business can be called up on GMB makes it worth the effort.
Therefore, having a verified, optimised and relevant GMB profile goes a long way and might be what you need to improve your SEO efforts.
11. Optimise for Voice Search and Mobile
With the advent of smart home devices like Amazon’s Alexa, and Google’s very own Google Home, what started out as a tool for accessibility and convenience is now rapidly becoming an important factor in SEO. Voice Search is garnering a ton of support as it allows for searches to be done quicker and with even more ease.
In the survey below, we can see the reasons why it is becoming popular.
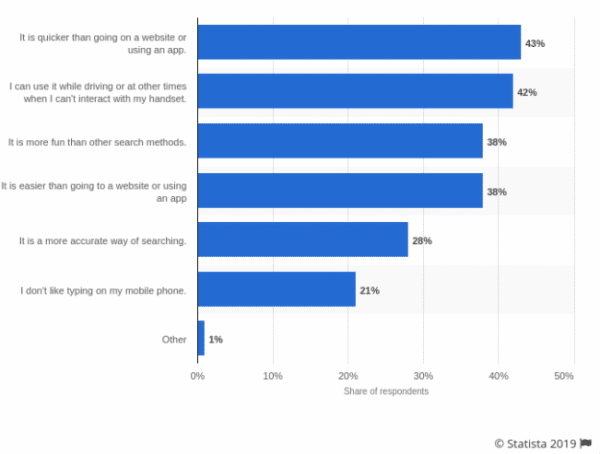
Reasons why Voice Search is preferred. Source: https://www.semrush.com/blog/voice-search-optimization-7-seo-strategies-to-rank-better/
They all point to one glaring reason: convenience.
With searches being done quicker in real-time, an increase in traffic is also natural. What’s more, 56% of all Voice Search is done via smart phones — which ties in with optimising your site to be mobile friendly, which we will discuss in a bit.
But first, how does voice search affect SEO?
Voice search results don’t work the same way as a standard SERP and the way we ask questions in voice search differs greatly from how we would type queries into a search engine.
Since people generally speak in longer, more complete sentences than they type into search engines, keywords for voice search have generally become longer. For example:
With typing, we would generally just search “how to make rice cakes”
With voice search, we might ask “Hey Siri, how do I make rice cakes at home?”
With our conversational queries, you can notice how the keywords differ. Moreover, voice searches are direct and prioritise listings near you, because as mentioned, the whole point is convenience. How this helps SEO is that it enables users to find you quicker, instead of having to sift through other results or pages that might not be relevant to them.
There are some key points to take note of when optimising your site for voice search.
People generally use search engines to find out about things. So, they ask a lot of questions, which logically suggests that Question Keywords should be targeted. Make sure to optimise your keywords for who, what, when, where, why and how queries.
While this is also done for normal search engine queries, the added factor to consider is that longtail keywords are what make up the bulk of voice search queries. Ensure you include these in your voice search keywords.
Filler words such as “I, the, on the, of the, to, for, from,” etc are a must to include, because these are part of conversations, and naturally they come up in voice searches too.
Remember that the majority of search traffic comes from smartphones. They are everywhere these days, and with the ease of access they grant, searches are made even more easily than before.
Optimising for Mobile
Ever since Google launched mobile-first indexing, sites that have not been optimised for mobile access get their rankings penalised because they aren’t easily viewable on phones. How does Google do this?
Simply put, they look at your site from the viewpoint of a mobile phone. You can try it out here.
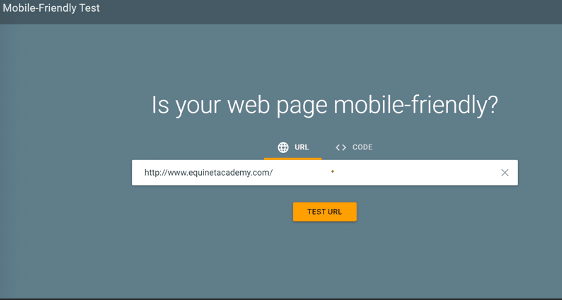
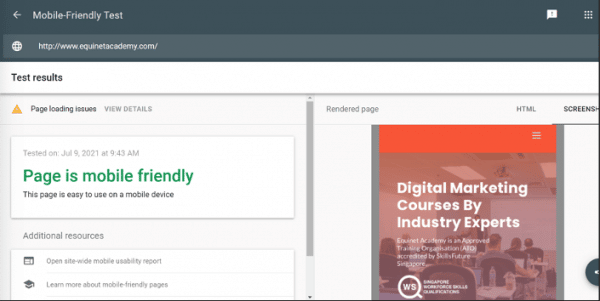
It’s very straightforward — it’s either yes or no. This couples with a list of suggestions for what you can do to improve your page as well.
How do you make your site mobile-friendly? Here are some ways you can go about it.
- Put in place a responsive web design, which serves users regardless of platform.
- Having different URLs can go a long way by offering codes on different URLs tagged to different devices.
- By using the same URL that generates differing HTML catered to different devices, you can dynamically serve different users.
Alternatively, you can consider:
- Updating your site to the latest version, and to mobile-friendly themes.
- On mobile devices, screens are smaller. So, make your CTAs and buttons are easily viewable.
- Duda has a great service for helping you create mobile-friendly platforms. Another service, Mobify, from Salesforce, helps to optimise your site for mobile devices as well.
With trends such as voice search and mobile optimisation here to stay, optimising for both will help your SEO rankings greatly.
Conclusion
SEO may seem tedious and very technical, but in truth it’s really simple if you follow the steps mentioned above. It contains tremendous growth potential if used right. Granted, you wouldn’t become a SEO expert overnight; but this should help you get started. Don’t be afraid to make mistakes as well.
So do take the time to look through your site and use the tips and tools above to your advantage.
Hopefully, this has given you better insight into improving your SEO ranking.
Additionally, if you are still unsure about how to get started, you might want to get some hands-on practice with our very own Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) Training Course. This is part of our Certified Digital Marketing Strategist (CDMS) Programme, which offers a holistic understanding and foundation in today’s Digital Marketing era.
The courses offered under the CDMS programme are:
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Content Marketing Strategy
- Search Engine Optimisation
- Digital Advertising
- Social Media Marketing
- Digital Marketing Analytics with Google Analytics
Upon completion of these modules, you will attain a Certified Digital Marketing Strategist Certificate from Equinet Academy.
We also offer an array of other digital marketing courses taught in-person in Singapore or online.
Kevin started in digital marketing, specialising in Search Engine Optimisation after leaving a career in banking and finance. He now has almost 10 years of experience gathering thousands of auditing hours on 300+ websites in all industries such as F&B, finance, insurance, e-commerce, medical and b2b services, serving clients such as MSIG Insurance, Bizcover Insurance, TWG Tea, Aura Group, Merger Markets (Acuris) and dozens of local SME’s, across Australia, New Zealand, Hong Kong, the United States and Singapore.