10 SEO Copywriting and Content Writing Best Practices
New to Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)? Check out our detailed guide on what it is here.
Ranking your website on the first page of Google isn’t as straightforward as it was back then (before Hummingbird and RankBrain changed the way Google evaluated and ranked content).
Way back in the early days of Google and up till 2012, in order to rank your website prominently on top of the search engines, you just had to include your target keywords in your content (meta tags, headlines, copy, etc.) and get a ton of keyword-rich anchor text backlinks from external webpages (usually spammy article directories) with high PageRank.
Try the latter now and risk getting slapped with a manual penalty.
Today, you actually need to have solid content that’s extremely useful and relevant for your target ranking keywords in order to nudge your way up to the top of the search results. Stuffing your title tags and content with keywords and building a ton of backlinks alone won’t cut it.
With the uprising trend of voice search (approximately 20% of mobile searches are now voice searches), Google has revolutionised the way search engines understand content and deliver search results to users.
For instance, keywords in the title tag no longer need an exact match to the search query for the page to rank well.
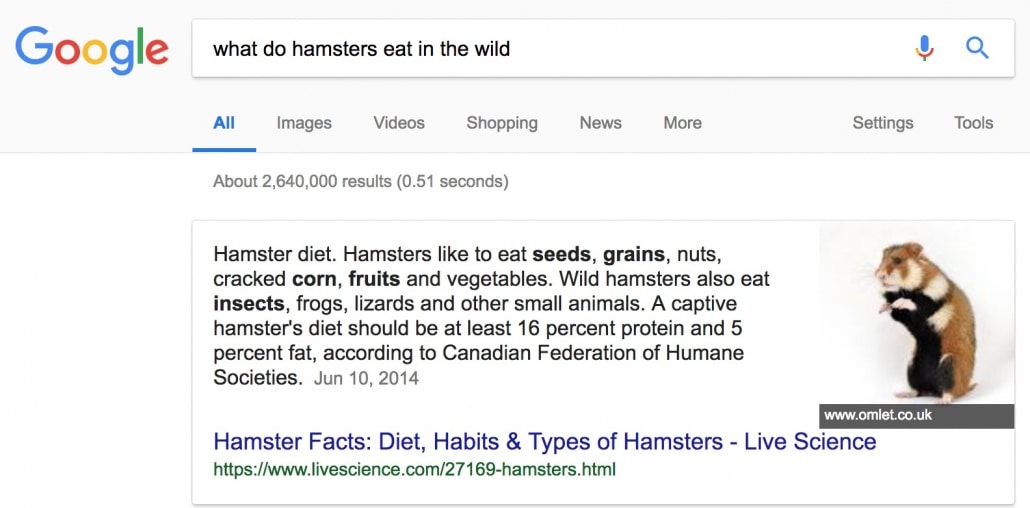
Google Search results – non-exact title tag to search query matching results
In the case of the search query “what do hamsters eat in the wild”, the title tag (in blue) matched only one keyword from the search query – hamster.
The rest of the search query keywords were found deep in the content body of the article. Yet, it was still able to rank on the featured answer box on top of the Google search results page.
This isn’t to say you shouldn’t still follow traditional SEO copywriting best practices like keyword inclusion (they still work to a certain extent).
Rather, you should adopt a healthy balance of writing and optimising content for both humans and search engines. Prioritise for humans however, as search engines were fundamentally built to serve humans and are continuously evolving towards serving humans better.
With that in mind, here’s a list of SEO best practices to adopt when you craft your next content masterpiece.
SEO Copywriting and Content Best Practices
To stand a good chance in ranking well on Google, ensure the following SEO best practices are met:
- Content is unique and more useful (solves the searcher’s query) than any result already on the first page
- Content and content format is relevant to the searcher’s intent and snippet entices clicks
- Group similar-themed keywords on one page rather than focusing on one keyword per page
- Include target keywords in the copy, images, meta tags, and URL
- Use markup where necessary (e.g. Schema, AMP, hreflang, opengraph)
- Page loading speed is fast < 3 seconds
- Page is device responsive without mobile intrusive interstitials
- Page content is accessible and crawl-able – adopt good internal linking practices
- Website is secured with HTTPS
- Content is amplify-able (easily earns social shares, mentions, and backlinks)
The above list pretty much sums up the what you need to do in order to stay on top of Google in 2019. Let’s break down each SEO best practice in more detail.
1. Content is unique and more useful (solves the searcher’s query) than any result already on the first page
Have you ever clicked on a search result and after skimming through it in the first 10 seconds, found that it didn’t answer your questions and clicked back to the search results page? That’s pogo-sticking.
Since RankBrain was deployed, user experience signals have become more and more important than off-page signals i.e. backlinks.
As a result, dwell time or the average time users spend on a webpage has been correlated to higher rankings. Meaning, the opposite is also true.
If users spent less time on search result A compared to search result B, they most probably did not find search result A very useful. Over time, Google will rank search result B above A.
Content uniqueness – ensure your content isn’t copied from elsewhere on the web. If it is ripped off entirely from another publication, Google will consider it duplicate content and it won’t rank well.
What can you do?
Conduct a search on your target keyword and analyse the top 5 results. Click into each result and digest each content. Then ask yourself, is there any unique value you can add to the question/search query? Can you develop content that’s 10 times more shareable and linkable?
Check out our list of 120 content types you can use for your next marketing campaign.
2. Content and content format is relevant to the searcher’s intent and snippet entices clicks
Imagine typing in “currency converter calculator” into Google and the first result (like the one below) explains how to use the tool rather than the actual tool for you to use.

Example of Google Search Result returning irrelevant query for currency converter tool
Though it may be relevant to the query (as in the keywords match), the result may not be relevant to the searcher intent. Most users would skip the first result and click on the tool in the second result like the example below. Note that higher click through rates (CTR) correlate to higher rankings.

Currency converter calculator search result
They would spend more time on the second result (xe.com) since they would be actively using the tool, resulting in a higher dwell time – higher dwell times correlate to higher rankings.
However, in the above case, since the searcher is looking for a tool to use, long form content is not an essential ranking factor.
In another scenario, if your search query is “how to bake cheese tarts”, the most relevant content formats would be a step-by-step recipe guide and/or a how-to video tutorial.
For generic search queries that are one or two words in length, it can be difficult to determine the exact intent. In this case, Google’s Query Deserves Diversity (QDD) algorithm kicks in and returns diversified results.
For example, the query “shoes” returns local map search results, a definitive article on shoes, and an e-commerce store selling shoes.
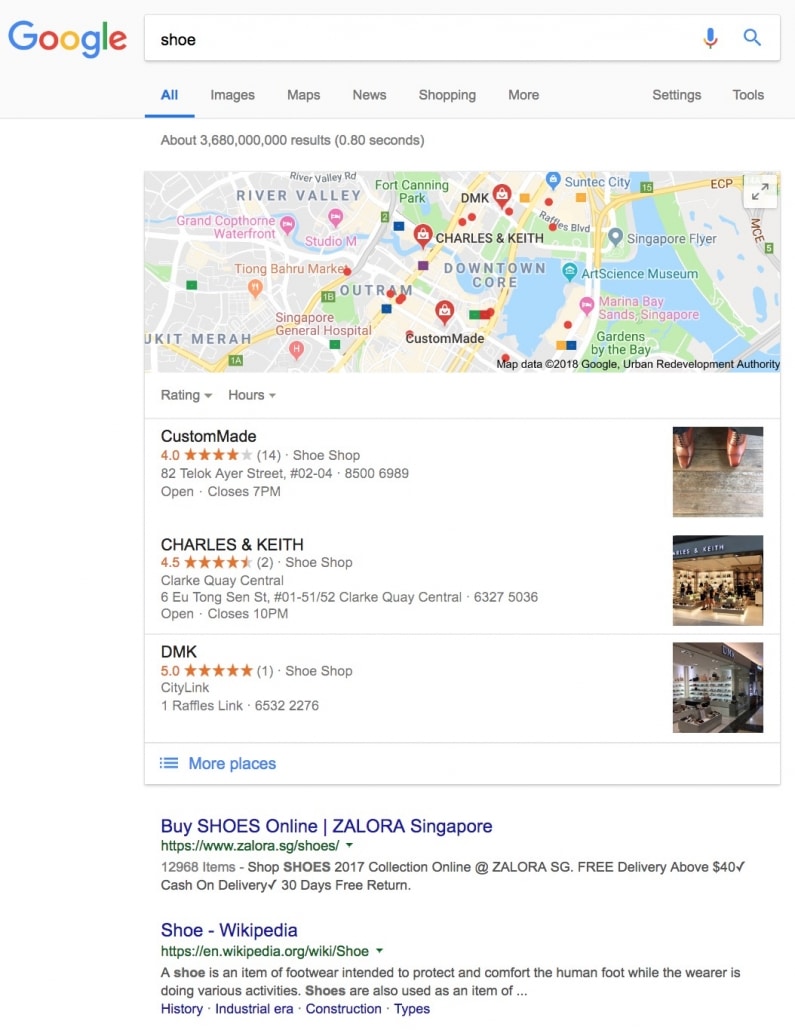
Shoe query
Certain queries also deserve freshness (see Google’s freshness algorithm). If the intent of a particular query was, say “taylor swift’s new boyfriend 2018”, an article on Taylor Swift’s new boyfriend in 2017 won’t make it to the top.
What can you do?
Take some time to reflect and analyse your target keywords in order to understand the searcher intent. Next, determine the most suitable content format (e.g. video, brand landing page, blogpost, services page, category listing, tool, fresh and up-to-date, etc.). Finally, apply creative copywriting skills to make your snippet enticing enough to click through.
3. Group similar-themed keywords on one page rather than focusing on one keyword per page
Again, with RankBrain as Google’s third most powerful ranking factor, we are seeing single page URLs ranking for more and more similar-themed keywords.
For instance, this page ranks for over 157 keywords.
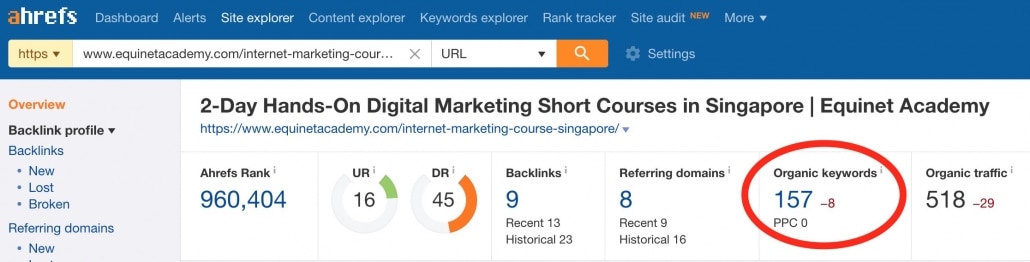
Equinet Academy organic search engine ahref organic keyword report
Let’s have a look at how similar the theme of these keywords are:
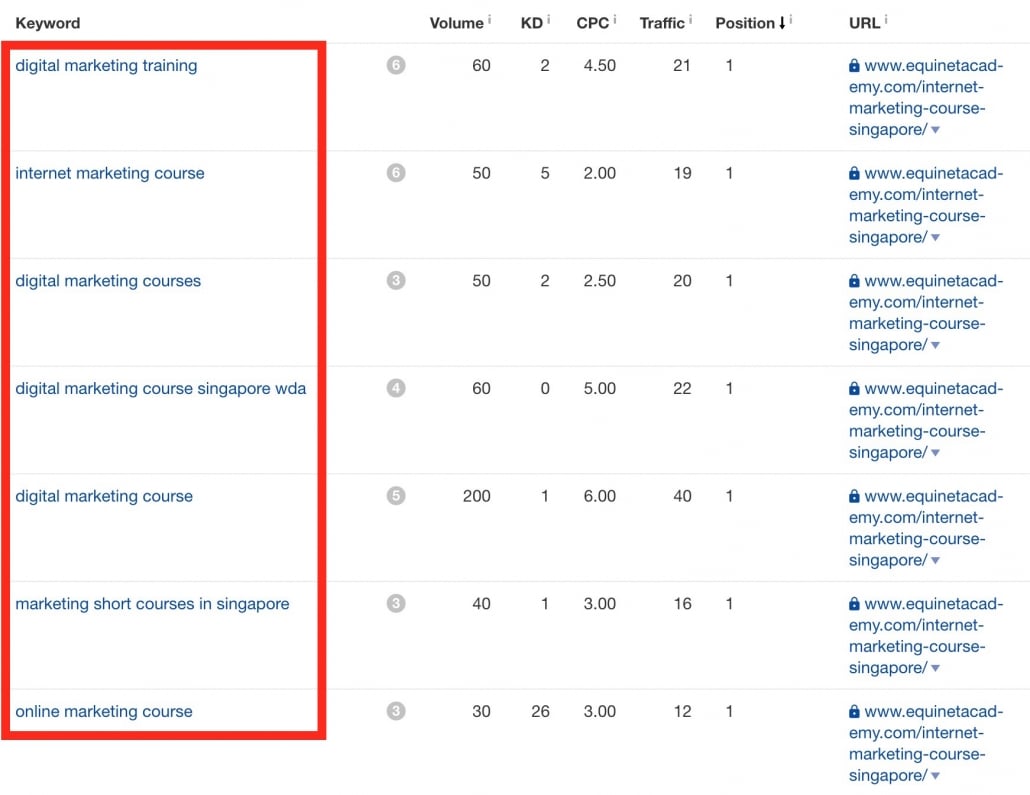
similar themed keywords ranking same page
As you can see, instead of creating one page for “digital marketing training”, one for “internet marketing courses”, and another one for “marketing short courses in singapore”, Google recognises the page is relevant for all these terms and ranks the same page on top for all of them.
What can you do?
Adopt a systematic approach to your keyword research process to group similar-themed keywords on one webpage.
Track and monitor your keyword rankings for the page.
If there is a huge disparity in ranking position between the keywords (i.e. one keyword is on position 1 while another keyword is on position 80), then the lower ranking keywords may need to be moved to another page.
4. Include target keywords in the copy, images, meta tags, and URL
Yes, this best practice has been around since more than two decades ago. The thing is, it still works.
Even though very few voice search results have the exact search query in the title tag, Google still tends to extract voice search answers that match the search query from within the copy.
Images also tend to rank better in Google Image search results when tagged with the keywords in the image file name and alternate tags.
Google tends to show the written meta description only when the search query is found in it.
What can you do?
Be sure to include your target keywords in the:
- Title tag
- URL
- Meta description
- Subheadings (H1, H2, H3…)
- Image alt tags and image file name
- Copy
- Internal links
5. Use markup where necessary (e.g. Schema.org)
Google works hard to understand the content of a page. You can help Google understand your content better by including structured data on your pages.
For instance, if you’re writing an article, you can mark up your content with structured data elements and describe the article or video there. This can help your content gain placement in the Top stories carousel and other rich result features.
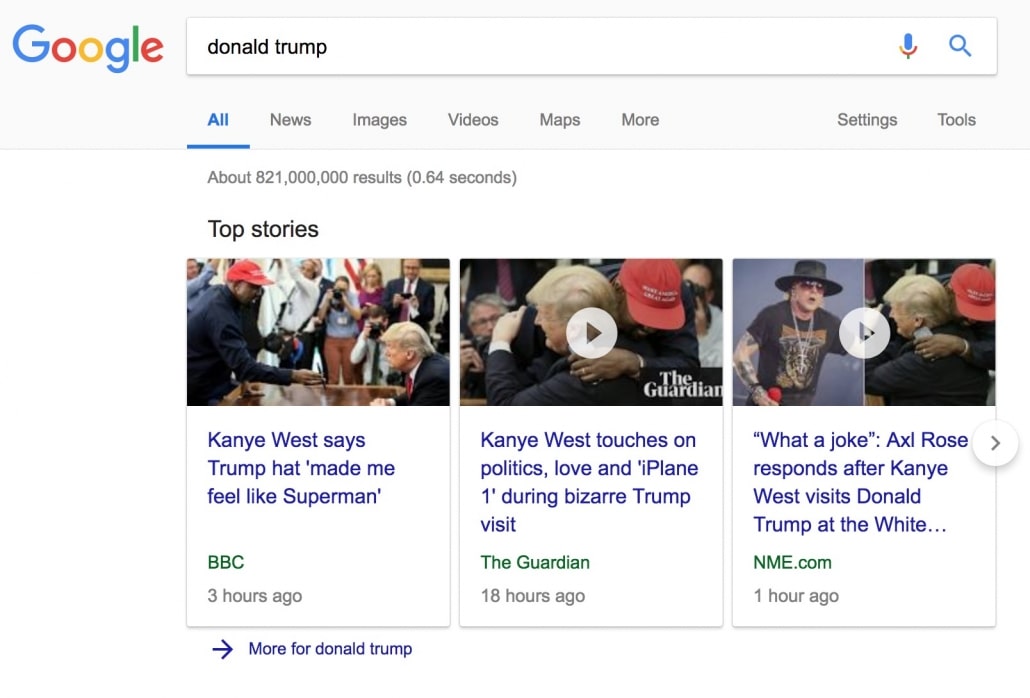
Top stories carousel
What can you do?
Check out developers.google.com to identify types of content items that can be marked up.
6. Page loading speed is fast < 3 seconds
Ever landed on page that took forever to load? You most probably became disinterested and hit the back button after the 6th second. Studies have shown that the probability of a user bouncing off a page increases 106% from 1 – 6 seconds of page loading time.
Page speed has also been confirmed as a ranking factor by Google for mobile searches.
What can you do?
Check your site with the PageSpeed Insights – Google Developers tool to diagnose slow loading issues such as large CSS files and images and optimise them. Develop accelerated mobile page (AMP) version of your articles.
7. Page is device responsive without mobile intrusive interstitials
Mobile searches are dominating desktop searches at a rate of over 60%, and it’s still growing fast. If your website still doesn’t load properly on mobile and tablet devices, your mobile rankings will be suffering by now.
Google has also confirmed the rollout of mobile intrusive interstitials penalty in January 2017. So, be sure to avoid interstitials such as these.

Types of Mobile Interstitials to avoid – Source: Google Webmaster Central
What can you do?
Check out whether your pages are mobile friendly with the mobile-friendly test tool by Google. Link your website up with Google Search Console to be notified of any mobile-related design and development issues.
8. Page content is accessible and crawl-able
Search engine spiders need to be able to access and crawl a page in order to properly index and rank it.
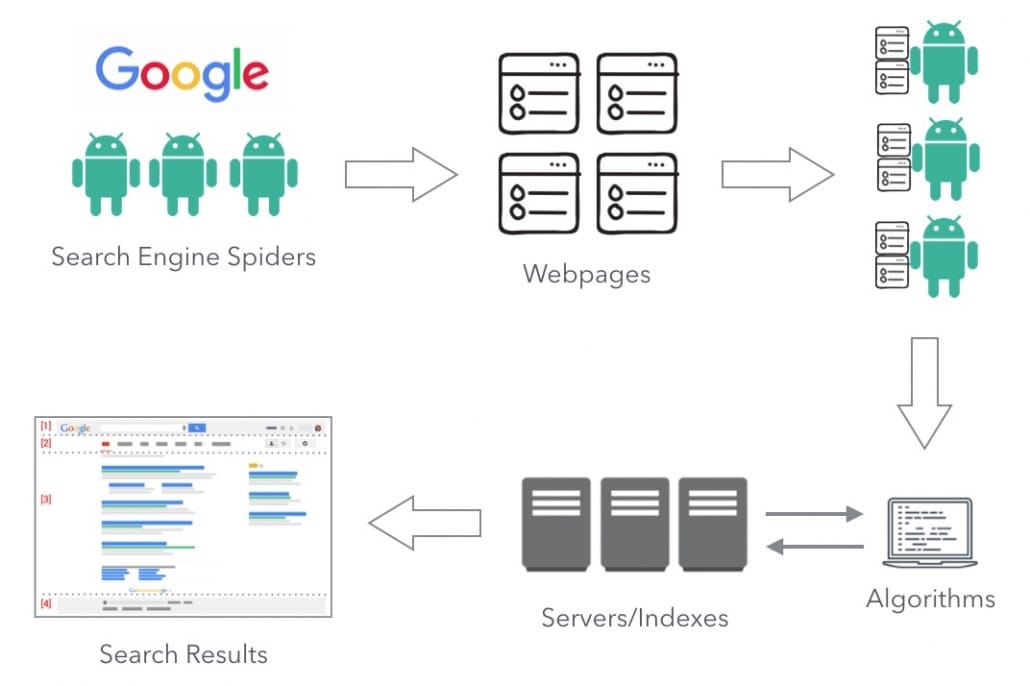
How search engines work
Here are some possible reasons why a page can’t be accessed or crawled:
- 4XX and 5XX errors – e.g. page cannot be found or server errors
- Too many redirects e.g. redirect chain or broken redirects
- Robots.txt file blocking crawlers from accessing a page
- Page is coded in web languages that search engines have problem understanding such as Flash or Java
Either way, if search engines can’t access or crawl your pages, they won’t rank well.
What can you do?
Conduct a full SEO website audit with an SEO auditing tool like Ahrefs Site Audit tool to identify webpages and web resources that can’t be accessed or crawled. Avoid having orphan pages – i.e. pages that have no links pointing to it. Be sure to submit a sitemap to Google Search Console and include more internal links between your pages where appropriate to ensure Google can easily discover them.
9. Website is secured with HTTPS
Google confirmed HTTPS as a ranking signal in 2014. Meaning, websites that have adopted HTTPS will see a slight boost in overall rankings.
What can you do?
Contact your web hosting provider or web developer to secure your site with HTTPS.
10. Content is amplify-able (easily earns social shares, mentions, and backlinks)
This is the last and one of the most important best practices to follow.
As Google relies on off-page signals to determine whether your content deserves to rank (though this factor has been decreasing in influence over the years), if your content isn’t Shareable, Mentionable, or Linkable (SML), it’ll be tough to maintain top rankings, much less rank on top of Google.
On the other hand, SML content not only tends to rank much higher, but also continuously earns publicity (in the form of shares, mentions, backlinks) the longer it stays on top.
Let’s have a look at an example. A resource page titled “What is SEO” by SearchEngineLand has a clear and comprehensive video explaining what SEO is. The quality of the content alone has allowed it to gradually gain backlinks over the last five years or so.
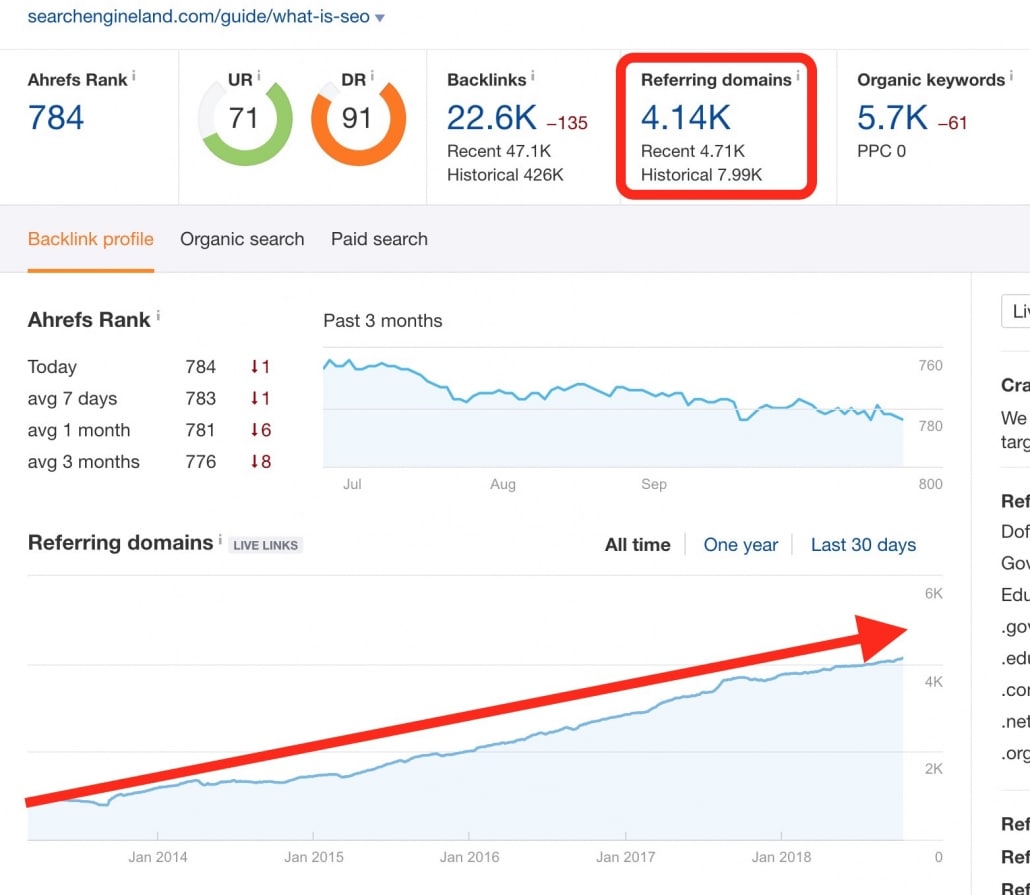
Steady growth in backlinks- referring domains report by Ahrefs tool
What can you do?
Get 10 people in your industry to read your content and ask them whether they would be open to share, mention, or link to it if there was an opportunity to do so. If the result is 0/10, it might be time to rethink the content.
Conclusion
Though Google’s algorithms continue to evolve (algorithm updates happen once or twice a day), the fundamental principles of good SEO remain the same:
- Provide high value content that’s relevant to the searcher’s intent
- Ensure your content is accessible and friendly to search engines and humans
- Amplify your content to earn social shares, mentions, and backlinks
Follow these SEO content best practices to rank well in 2019. Check out my other article on the 22 must-have elements in your blog post, with a bonus template for easy reference. Also, to know more about SEO and other Digital Marketing disciplines, at Equinet Academy we offer a range of digital marketing courses taught in-person in Singapore or online for you to up-skill yourself.
Dylan Sun is the Founder of Equinet Academy, a SkillsFuture Singapore WSQ-Accredited Digital Marketing training organisation. Passionate in all aspects of Digital Marketing and SEO, he extends his passion to helping people implement effective digital strategies to their businesses. Follow his blog at Equinet Academy to learn more about Digital Marketing.
Your article is much informative.The article helps the beginners a lot to learn.I like your post always.I humbly thank you for your kind information.
I am searching for the 2019 SEO trends and got this great article which is very informative and useful. I just want to update and implement the SEO strategies to my website for good results. As content is king, following your tips will definitely help me in ranking.
Thanks for sharing the information.