On-Page SEO – Keyword Optimisation Guide
With Search Engine Optimisation (SEO), keyword optimisation comes after you have conducted keyword research and built your list of target keywords. (Free bonus On-Page SEO Keyword Optimisation Cheatsheet here.)
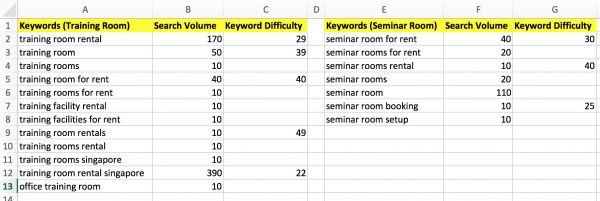
Here’s a sample of a raw keyword research list in excel format:
So what we’re essentially doing here is taking these keywords and placing them into key areas of your website. They are:
- Title Tags
- Domain Name and URL
- Meta Description
- Images
- Content
1. Title Tags (Best Practices)
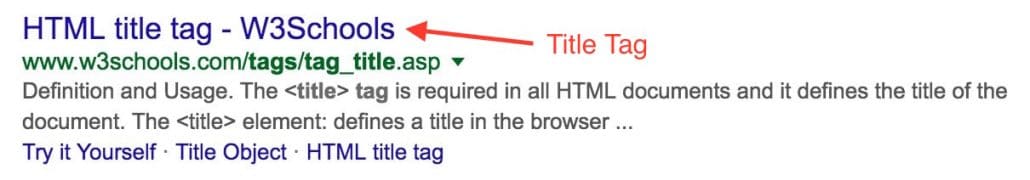
Title Tags <title>Example Title</title> tell search engines what your page is about. Search engines may then use your title tags to display your page title on the search results snippets.
If your website is on WordPress.org, install the Yoast SEO plugin to enable the Title Tag field to fill in your title tags. If you’re on other content management systems, there should be a built-in SEO title box/field or an extension to enter your title tags.
Here are some SEO best practices for your Title Tags:
- Place the keyword closer to the front of the title. Moz tested and concluded that this increases the likelihood of a user clicking on the search result and also helps in search engine rankings.
- Ensure your title is unique, outstanding, and appealing. Cross check with competitor sites and your own internal page titles. Consider the searcher intent and make your title appeal to their emotions. The more appealing the title, the higher the click-through-rate. Search engines also place importance in the uniqueness of your title.
- Keep the length of your title between 50 – 60 characters / 512 pixels wide. If the title is too long, search engines will truncate the titles and show an ellipsis.
- Include your brand name in the title tag. It is good practice to place your brand name in front on the title tag for the homepage and at the back for internal pages of your site. This increases brand exposure and the likelihood of a user (who has repeated seen the brand’s name) clicking on a particular brand’s search result.
- Optimise for multiple keywords. Optimising for multiple keywords increases the chances of ranking for more than one keyword. For example, business cards and name cards share similar meaning and can both be included in the title tags if there is sufficient space (512 pixels max).
2. Domain Name and URL (Best Practices)
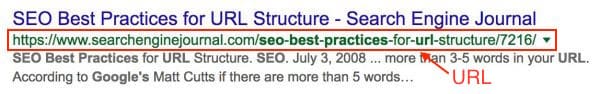
The domain name and URL appears in the search results snippets as well.
Exact match domain names (EMD) like classroomforrent.com no longer have significant direct impact on rankings after Google turned the knob down on EMDs in the recent years.
However having an EMD can indirectly impact rankings when external sites include a naked hyperlink (e.g. <a href=“http://classroom-rental.com>classroom-rental.com</a>) to your site, since keywords in the anchor text are considerably an important ranking factor.
Here are some SEO best practices for your domain name and URLs:
- Keep all sections of your site in one domain or subdomain. It is recommended to keep your important webpages in sub directories (e.g. example.com/blog/post/ as opposed to blog.example.com/post/) as search engines use different ranking metrics for domains and subdomains.
- Avoid nesting folders into deep layers e.g. www.example.com/folder1/folder2/folder3/example-content as search engine spiders may have trouble crawling deeper into your site. Search engines also tend not to crawl deeper into your site if you have a low domain authority.
- Include your keywords in your URLs. e.g. https://www.example.com/classroom-for-rent/
- Keep your domain name and URLs short and easy to understand (< 100 characters) and use lower case letters. This makes it easier for users to remember and type into the browser. Some users may not be exactly sure whether they have gotten the correct spelling of the domain name. Thus they would search for the domain name on Google instead of typing the full address.
- Consider removing “stop words” such as and, or, but, a, etc. Shorter URLs allow users to easily remember and type the full URL.
- Avoid rewriting dynamic URLs into static URLs e.g. (www.example.com/index.php?page=icdl-module&id=31). Though it is advisable to use static URLs as much as possible, in cases when you have dynamic content, it is recommended not to remove information (hiding parameters) to make them look static. To check whether Google has problems crawling your dynamic URLs, you can check for any issues/alerts in your GWT (Google Webmaster Tools) account.
- Use hyphens and underscores as word separators but avoid hyphens on domain names. Using hyphens and underscores (hyphens preferred) on your URLs is recommended. It helps indicate to search engines the number of keywords used in the URL. E.g. example.com/rentalounge/ should be written as example.com/rent-a-lounge/. On the other hand, domain names should avoid using hyphens as this is common practice among spammy websites. (e.g. class-room-rental-for-rent.com)
- Get HTTPS. Google has confirmed the use of HTTPS as a ranking signal. However it is now only a very lightweight signal compared to other signals such as high-quality content. It is still good practice to adopt HTTPS on your websites as Google may decide to strengthen this signal over time.
Further reading:
Keep a simple URL structure | Google Search Console Help
15 SEO Best Practices for Structuring URLs | Moz
3. Meta Description (Best Practices)
The meta description isn’t a ranking factor as stated by Google in 2007. It’s worth noting however, that meta descriptions can improve clickthrough (driving user traffic to your website).
Here are some SEO best practices for your meta description:
- Keep your meta description between 150 to 160 characters. If your meta description is too long, Google will truncate it.
- Include your target keywords in your meta description. This will make it more compelling for users to click when they see words that are relevant to their search query.
- Make your meta description is unique, outstanding, and persuasive. Treat the meta description as your ad text. Be sure to browse through the search results (both paid and organic results) and ensure yours is the most outstanding and has the most compelling value proposition.
- Ensure it is wrapped around the meta tags. <meta name=”description” content=“Example meta description content that will often show up in the search results snippets.”> and placed in the <head></head> section. For WordPress sites, use the Yoast SEO plugin to easily add a meta description.
- Use only alphanumeric characters in your meta description. If wrapped in quotes “ ”, Google won’t display it.
- Use structured data markup if it is appropriate to the content. (Use a WordPress rich snippets plugin if you are using WordPress, or hire a web developer if you wish to create your own snippets.)
4. Images (Best Practices)
Using images can help make your content livelier and also convey credibility (trust is an important factor for conversions). Avoid using overly-used stock photos. If you’re selling a product, include closeup photos of them. If you’re renting out a room, include professionally-taken photos of your rooms.
Here are some SEO best practices for your images:
- Use a descriptive image file name i.e. (car-showroom.jpg instead of DM9902.jpg). This will help Google understand your image better and help it rank better on Google Image Search.
- Make your alt tags descriptive of the image and include your target keywords when possible (do not stuff keywords). <img src=“http://example.com/uploads/car-showroom.jpg alt=“car showroom”>. This is a ranking factor and will help in your rankings.
- Reduce your image file sizes and use the right image file type (e.g. JPEG is preferred over PNG / GIF). Slow loading times can negatively impact your rankings.
- Use unique, high quality, custom graphics/photos where possible to increase chances of people embedding/citing your images. This will help in your link building efforts.
- Include your images into your sitemap and submit your sitemap to search engines. It will help search engines to crawl and index your images better.
5. Content (Best Practices)
Creating the best and most relevant answer for your target search queries is one of the best principles to stick by. Think of the search query as a question (also known as the searcher intent), and your content as the answer to the question, and you’ll be on the right track. We go further in-depth into content marketing in this article.
If someone were searching for “currency converter tool”, what would be the best thing to show up in front of her?
Yup, you got it. An online currency converter software like www.xe.com.
Content can come in many forms, including some of the following:
- Blogpost – Copy that’s a couple of hundred (or thousands of) words long and may include images, written in a friendly, second-person point of view style.
- Article – Online news reports, magazine, or a shortened form of a white paper are all examples of articles, written in a more serious tone as compared to a blogpost.
- Video – If someone were searching for “how to bake a cake tutorial”, a blogpost with a detailed step-by-step video detailing how to bake a cake from scratch would be a great answer.
- Product Page – A page zooming in on a product’s specific details on an e-commerce website.
- Listicles – Think of search terms like “best restaurants in my area”. What would be the most appropriate results? – Most probably content publishing sites like www.thesmartlocal.com featuring an blogpost titled, “21 Best Local Restaurants in Singapore”.
The list goes on and on…
Here are some SEO best practices for your content:
- Ensure your main content (MC) and supplementary content (SC) is relevant to your target keywords and provides the best answer to the searcher intent. This helps to minimise “pogo-sticking” (where a visitor bounces back to the search results pages right after clicking on a search result), as visitors expect to see a relevant and useful content after clicking on a search result.
- Mention your primary and secondary keywords early on in your copy. It is good SEO practice to mention your primary and secondary keywords in the first paragraph of your copy. This signals to search engines that your content is relevant to your target keywords mentioned in your title.
- Primary and secondary keywords should be included in subheadings and distributed evenly throughout your copy. On the other hand, stuffing your target keywords on every paragraph of your copy can be a signal of spam and get your pages penalised by search engines.
- Ensure your content is unique and has E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). Write like you’re the subject matter expert and worry about keyword optimisation later. These are indicators which Google uses to access the quality of your content and are used in their ranking algorithms.
- Link out to relevant internal pages of your website or relevant external websites where appropriate. To improve your pages’ relevancy score and help search engines understand the topic of your pages and index them better, link each page back to its category or subcategory pages, related internal pages of your site, and external relevant and reputable sources.
Key Takeaways
- Conduct in-depth keyword research prior to keyword optimisation so that you won’t miss out placing any important keywords in your title, URL, meta description, images, and content.
- Always be relevant when choosing keywords to optimise for. You don’t want to confuse users by showing them keywords that aren’t relevant to their search queries. For this, you need to really understand the intent of the search queries (searcher intent).
- Do not spam or stuff keywords. Instead, develop your content naturally first and get a subject matter to craft your content. Worry about placing your target keywords in your copy later.
There’s a fine line between optimising your pages for search engines and catering to humans. If you optimise your content too heavily, you risk speaking to search engines rather than writing in human language. If you totally ignore how search engines rank your content, you’ll miss out on optimising for the right keywords.
As SEOs, we have to be creative, resourceful, and flexible in order to keep both search engines and humans happy.
Here’s a free bonus On-Page SEO Keyword Optimisation Cheatsheet you can reference the next time you’re keyword-optimising your webpages.
If you’d like to learn SEO to level-up as a digital marketer or business owner, feel free to enrol in our Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) Training Course, or even our Advanced Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) Certification Course. We also offer an array of digital marketing courses taught in-person in Singapore or online.
Dylan Sun is the Founder of Equinet Academy, a SkillsFuture Singapore WSQ-Accredited Digital Marketing training organisation. Passionate in all aspects of Digital Marketing and SEO, he extends his passion to helping people implement effective digital strategies to their businesses. Follow his blog at Equinet Academy to learn more about Digital Marketing.


Thanks for the useful guide and the free SEO optimisation check-sheet.
Your guide is comprehensive enough for newbies like me to do own SEO optimisation on my websites.
Hey Rahman, thanks for stopping by and great to hear from you again. Hope to see you around for the SEO mentorship sessions at Equinet.